TypeNameList=`default`:`type`,`default2`:`type`
Couchbase Translator
The Couchbase Translator, known by the type name couchbase, exposes querying functionality to Couchbase Data Sources. The Couchbase Translator provide a SQL Integration solution for integrating Couchbase JSON document with relational model, which allows applications to use normal SQL queries against Couchbase Server, translating standard SQL-92 queries into equivalent N1QL client API calls. The translator translates Teiid push down commands into Couchbase N1QL.
Usage
The Couchbase Translator supports INSERT, UPSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, SELECT and bulk INSERT statements with a restrictive set of capabilities including: count(*), comparison predicates, Order By, Group By, LIMIT etc. Consider a custom extension or create an enhancement request should your usage require additional capabilities.
If you are using Designer Tooling, to create VDB then:
-
Create/use a Teiid Designer Model project
-
Use "Teiid Connection >> Source Model" importer, create a new JBoss Data Source connection profile, specifying the JNDI name for resource adapter configured Couchbase Data Sources and use couchbase as translator type. The source model will be created when you finish with this importer.
-
Create a VDB and deploy into Teiid Server and use either jdbc, odbc, odata etc to query.
JCA Resource Adapter
The Teiid specific Couchbase Resource Adapter should be used with this translator. See Couchbase Data Sources for connecting to a Couchbase cluster.
Execution Properties
Use the translator override mechanism to supply the following properties.
| Name | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
UseDouble |
Use double rather than allowing for more precise types, such as long, bigdecimal, and biginteger. This affects both import and execution. See the issue that describes problems with Couchbase and precision loss. |
false |
Schema Definition
Couchbase is able to store data that does not follow the rules of data typing and structure that apply to traditional relational tables and columns. Couchbase data is organized into buckets(keyspaces) and documents.

The document in a keyspace are structureless, it may have complex structure, like contain nested object, nested arrays, or arrays of differently-typed elements.
|
Note
|
The datastores are higher level abstraction, but the Couchbase Translator focus on one specific namespace, all documents in a namespace across different keyspaces will be map to tables of Teiid source metadata. |
Because Teiid metadata/traditional JDBC toolsets might not support these data structures, the data needs to be mapped to a relational form. To achieve this, the Couchbase Translator provide a way to automatically generates schema during VDB deploying. Refer to Generating a Schema for more details.
Alternatively, create the schema manually in a Teiid Source module are supported, creating a schema should base on the sample rules of generating a schema. Refer to Creating a Schema for more details.
|
Note
|
Use Generating a Schema are recommend. |
Generating a Schema
Schema Generation is a way that the Couchbase Translator sample some data from a Couchbase cluster(namespace), and scan these documents data, generate a data typing and structure based schema that is needed for Teiid or traditional JDBC toolsets. The Importer Properties are used to control the behavior of data sampling.
The generated schema are tables and procedures, the procedures provide additional flexibility to execute native query; the tables are used to map to documents in a specific namespace. There are two kinds of table,
-
Regular Table - map to a keyspace in a couchbase(namespace)
-
Array Table - map to a array in any documents
A table option used to differentiate Regular Table and Array Table, refer to Additional Table Options for details.
The principle use to generate schema are following:
-
Basically, a keyspace be map to a table, keyspace name is the table name, all documents' no-array attribute are column names, each document are a row in table. if
TypeNameListdefined, a keyspace may map to several tables, all same type referenced values are table names, all same type value referenced no-array attribute are map to column names correspondently. If multiple keyspaces has same typed value, the typed value table name will add each keyspace as prefix. For example,
both default and default2 has document defined {"type": "Customer"}, then the default’s table name is 'Customer', default2’s table name is 'default2_Customer'.
-
Each generate table has a documentID column map to a couchbase document ID, the documentID in Regular Table play a role as primary key, the documentID in Array Table play a role as foreign key.
-
Any of array in documents will be map to a Array Table, array index, array item or nested object item attribute are column names. If array contains differently-typed elements and no elements are object, all elements be map to same column with Object type; If array contains object, all object attribute be map to column names, and reference value data type be map to column data type;
-
Each Array Table has at least one index column with the suffix
_idxto indicate the position of the element within the array. If the dimension of array large than 1, multiple index column are created, the column name with explicity dimension identity_dimX, separated by underscore character. For example, a three dimension nested array document
"default": {"nested": [[["dimension 3"]]]}the index columns might like: default_nested_idx, default_nested_dim2_idx, default_nested_dim2_dim3_idx.
-
Each Table must define a NAMEINSOURCE to indicate the keyspace name or he path pattern in couchbase, the NAMEINSOURCE of Regular Table are keyspacename, the NAMEINSOURCE of Array Table are path pattern with square brackets suffix to indicate dimension of nested array. Use above three dimension nested array document as example, the NAMEINSOURCE of table might be
default.nestedArray[][][]. -
Each no documentID, no array index columns must be define a NAMEINSOURCE to indicate the path pattern in couchbase, the dot are use to separate the paths. For example, the
p_asiaare nested object attribute of a document in keyspacetravel-sample:
default:`travel-sample`/geo/`p_asia`the p_asia referenced column must define a NAMEINSOURCE with value travel-sample.geo.p_asia.
The Array Table column’s NAMEINSOURCE must use a square brackets for each hierarchy level in which dimension the array is nested. For example, the nestedArray are nested array attribute of a document in keyspace travel-sample, it’s dimension 3 nested array at least has two items, dimension 4 nested array at least has two items:
default:`travel-sample`/nestedArray[0][0][1][1]the dimension 4 nested array coulmn must define a NAMEINSOURCE with value travel-sample.nestedArray[][][][]. If dimension 4 item has object item, then the coulmn NAMEINSOURCE might be travel-sample.nestedArray[][][][].id, travel-sample.nestedArray[][][][].address_name, etc.
-
If a table name defined by TypeNameList, another NAMEDTYPEPAIR option are used to define the type attribute, more details refer to Additional Table Options.
Importer Properties
To ensure consistent support for your Couchbase data, use the importer properties to do futher defining in shcema generation.
<model name="CouchbaseModel">
<property name="importer.sampleSize" value="100"/>
<property name="importer.typeNameList" value="`test`:`type`"/>
<source name="couchbase" translator-name="translator-couchbase" connection-jndi-name="java:/couchbaseDS"/>
</model>| Name | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
sampleSize |
Set the SampleSize property to the number of documents per buckets that you want the connector to sample the documents data. |
100 |
sampleKeyspaces |
A comma-separate list of the keyspace names, used to fine-grained control which keyspaces should be mapped, by default map all keyspaces. The smaller scope of keyspaces, the larger sampleSize, if user focus on specific keyspace, and want more precise metadata, this property is recommended. |
* |
typeNameList |
A comma-separate list of key/value pair that the buckets(keyspaces) use to specify document types. Each list item must be a bucket(keyspace) name surrounded by back quotes, a colon, and an attribute name surrounded by back quotes. .Syntax of typeNameList `KEYSPACE`:`ATTRIBUTE`,`KEYSPACE`:`ATTRIBUTE`,`KEYSPACE`:`ATTRIBUTE`
For example, the TypeNameList below indicates that the buckets(keyspaces) test, default, and beer-sample use the type attribute to specify the type of each document, during schema generation, all type referenced value will be treated as table name. TypeNameList=`test`:`type`,`default`:`type`,`beer-sample`:`type` The TypeNameList below indicates that the bucket(keyspace) test use type, name and category attribute to specify the type of each document, during schema generation, the teiid connector scan the documents under test, if a document has attribute as any of type, name and category, it’s referenced value will be treated as table name. TypeNameList=`test`:`type`,`test`:`name`,`test`:`category` |
N/A |
Additional Table Options
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
teiid_couchbase:NAMEDTYPEPAIR |
A |
teiid_couchbase:ISARRAYTABLE |
A
|
Creating a Schema
Creating a schema should strict base on the principles listed in Generating a Schema.
Couchbase supported Teiid types are String, Boolean, Integer, Long, Double, BigInteger, and BigDecimal. Creating a source model with other types is not fully supported.
Each table is expected to have a document ID column. It may be arbitrarily named, but it needs to be a string column marked as the primary key.
An example of Schema Generation
The following example shows the tables that the Couchbase connector would generate if it connected to a Couchbase, the keyspace named test under namespace default contains two kinds of documents named Customer and Order.
The Customer document is of type Customer and contains the following attributes. The SavedAddresses attribute is an array.
{
"ID": "Customer_12345",
"Name": "John Doe",
"SavedAddresses": [
"123 Main St.",
"456 1st Ave"
],
"type": "Customer"
}The Order document is of type Order and contains the following attributes. The CreditCard attribute is an object, and the Items attribute is an array of objects.
{
"CreditCard": {
"CVN": 123,
"CardNumber": "4111 1111 1111 111",
"Expiry": "12/12",
"Type": "Visa"
},
"CustomerID": "Customer_12345",
"Items": [
{
"ItemID": 89123,
"Quantity": 1
},
{
"ItemID": 92312,
"Quantity": 5
}
],
"Name": "Air Ticket",
"type": "Order"
}When the VDP deploy and load metedata, the connector exposes these collections as two tables show as below:
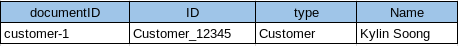

The SavedAddresses array from the Customer and the Items array from the Order document do not appear in above table. Instead, the following tables are generated for each array:

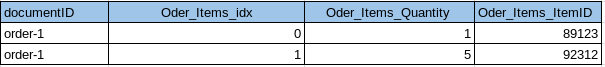
Procedures
Native Queries
Couchbase source procedures may be created using the teiid_rel:native-query extension - see Parameterizable Native Queries. The procedure will invoke the native-query similar to a direct procedure call with the benefits that the query is predetermined and that result column types are known, rather than requiring the use of ARRAYTABLE or similar functionality.
EXEC CouchbaseVDB.native('DELETE FROM test USE KEYS ["customer-3", "order-3"]')getDocuments
Returns the json documents that match the given document id or id pattern as BLOBs.
getDocuments(id, keyspace)-
id - The document id or SQL like pattern of what documents to return, for example, the '%' sign is used to define wildcards (missing letters) both before and after the pattern.
-
keyspace - The keyspace name used to retrieve the documents.
call getDocuments('customer%', 'test')getDocument
Returns a json document that match the given document id as BLOB.
getDocument(id, keyspace)-
id - The document id of what document to return.
-
keyspace - The keyspace name used to retrieve the document.
call getDocument('customer-1', 'test')