<vdb name="my-example" version="1">
<model name="test" type="PHYSICAL">
<property name="importer.schemaPattern" value="public"/>
<property name="importer.useFullSchemaName" value="false"/>
<property name="importer.tableTypes" value="TABLE,VIEW"/>
<source name="pqsql" translator-name="postgresql" connection-jndi-name="java:/postgres-ds"/>
</model>
</vdb>Virtual Databases
A virtual database (or VDB) is a metadata container for components used to integrate data from multiple data sources, so that they can be accessed in an integrated manner through a single, uniform API.
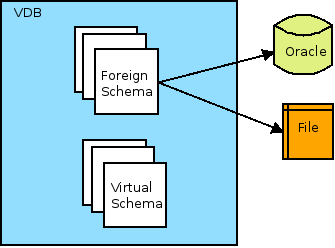
A VDB typically contains multiple schema components (also called as models), and each schema contains the metadata (tables, procedures, functions). There are two (2) different types of schemas
-
Source Schema (also called Physical or Foreign schema), which represents an external/remote data sources like Relational database (Oracle, DB2, MySQL..), Files(CSV, Excel..), Web-Services(SOAP, REST) etc.
-
Virtual Schema. This is a view layer or logical schema layer, that is defined using schema elements from Foreign Schemas. For example, creating a view table using multiple foreign tables from different sources, thus hiding the complexities of definition of the view from user.
One important thing to note is, a VDB ONLY contains metadata, NEVER copies/has the actual data. Any usecase involving Teiid MUST have a VDB to begin with. So, it is very important to learn how a VDB can be designed/developed.
Below is an example VDB, that is using a single foreign schema component defining a connection to PostgreSQL database.
Another variation of the VDB using completely DDL and using SQL-MED specification.
CREATE DATABASE my_example VERSION '1.0.0';
USE DATABASE my_example VERSION '1.0.0'
CREATE FOREIGN DATA WRAPPER postgresql;
CREATE SERVER pgsql TYPE 'postgresql-9.4-1201.jdbc41.jar'
VERSION 'one' FOREIGN DATA WRAPPER postgresql
OPTIONS (
"jndi-name" 'java:/postgres-ds'
);
CREATE SCHEMA test SERVER pgsql;
IMPORT FOREIGN SCHEMA public FROM SERVER pgsql INTO test
OPTIONS(
importer.useFullSchemaName false,
importer.tableTypes 'TABLE,VIEW'
);Both formats define the same VDB.
There is lot to be explained from above examples, in the following sections, we will go into detail about each of those lines. Before that we need to learn about further fractions in the Source Schema component.
External Data Sources
A "source schema" component in VDB as shown in above example is a collection schema elements as tables, procedures and functions that represent an external data source’s metadata locally. However in the above example, it did not define any such schema elements, however details of connection to the external data source were provided through "jndi-name", which is a named connection reference to a external data source.
For the purposes of Teiid, connecting and issuing queries to fetch the metadata from these external data sources, Teiid defines/provides two types of resources.
Resource Adapter
A resource adapter (also called as SERVER) is connection object to the external data source. In the case of relational database this can be achieved through a JDBC connection, or in the case of a File this may be a reference to file’s location. The resource-adapter provides a unified interface to define a connection in the Teiid. A resource adapter also provides way to natively issue commands and gather results. Teiid provides variety of resource adaptors to many different systems or one can be developed for new/custom data source. A resource adapters connection is represented above as the "jndi-name".
As VDB developer you need to know, how to configure these sources in the Teiid. In WildFly Server these are defined as JCA components. In Teiid embedded, the developer has to define the connections to these sources programmatically. Check out Administrator’s Guide on how to configure these in WildFly, or embedded examples, if you are working with Teiid Embedded.
Translator
A Translator (also called DATA WRAPPER) is a component that provides an abstraction layer between Teiid Query Engine and physical data source, that knows how to convert Teiid issued query commands into source specific commands and execute them using the Resource Adapter. It also have smarts to convert the result data that came from the physical source into a form that Teiid Query engine is expecting. For example, when working with a web-service translator, a SQL procedure executed at Teiid layer may be converted to a HTTP based call through a translator, and response JSON could be converted to tabular results.
Teiid provides various translators as part of the system, or one can be developed using the provided java libraries. For list of available Translators see Translators
|
Important
|
In a VDB, a source schema must be configured with a correct Translator and a valid resource adapter, to make the system work. |